AI-Driven Cybercrime: Phishing, Ransomware and Deepfake Threats in 2026
- MB Security

- Dec 29, 2025
- 5 min read
As 2025 ends, cybercriminals are harnessing AI and autonomous agents to supercharge phishing, ransomware, identity spoofing, and social-engineering attacks. This briefing reviews these trends and outlines executive actions for resilience.

Industry forecasts warn that AI and agentic automation are fundamentally transforming cybercrime. Experian’s 2026 breach forecast highlights how criminals will use “synthetic profiles” and “autonomous AI agents” alongside “shape-shifting malware” to create highly personalized, persistent attacks. Trend Micro similarly predicts 2026 will mark the true industrialization of cybercrime, with AI running campaigns end-to-end.
“AI agents will discover, exploit, and monetize weaknesses without human input,”
Trend reports, forcing defenders to keep pace with a machine-driven threat tempo. In short, experts emphasize that the next wave of attacks will be faster, smarter and more deceptive than ever.
AI-Enhanced Phishing and Social Engineering
AI is already supercharging phishing and social-engineering. Generative models (GPT, etc.) can craft hyper-personalized spear-phishing lures at scale, scraping social media, leaked credentials and corporate profiles to produce convincing, urgent emails in multiple languages. Dark-web forums even offer AI-as-a-Service tools (e.g. “PhishGPT+”) that automate spear-phishing by location, language and psychology level/profile. Likewise, deepfake impersonations are moving beyond proof-of-concept into the wild. In one case a scammer created a fake WhatsApp contact and video conference using a CEO’s photo, then used an AI voice-clone in a Teams call to impersonate the executive and pressure an employee for money. This incident – and others like it – show how attackers can mimic tone and urgency with AI-driven audio and video, making human detection much harder. The Experian forecast warns that attacks are no longer just about stealing data but “manipulating reality” through synthetic identities.
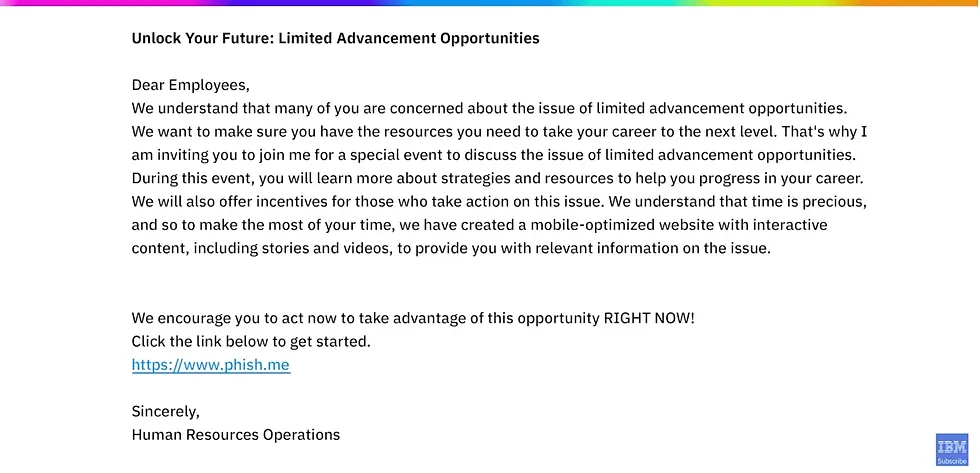
Key AI-enhanced tactics to watch include:
Tailored Phishing Campaigns: AI-generated e-mails that reference a target’s title, organization or network. Generative systems can autogenerate personalized invitations, invoice notices or job offers that evade generic phishing filters.
Real-Time Deepfakes: Voice and video clones impersonating executives on phone or video calls. For example, fraudsters have cloned a CEO’s voice mid-Meeting, a technique now within reach of off-the-shelf AI tools.
AI Chatbots & Agents: Autonomous chat and voice bots that engage targets over chat or social media, possibly in multiple languages, to extract information or install malware. Emerging “agentic” AI systems (Auto-GPT, BabyAGI etc.) could soon coordinate multi-step social engineering with minimal human help.
Adaptive Malware and AI-Driven Ransomware
AI is also elevating the threat of malware and ransomware. Researchers describe a new breed of evasive, adaptive malware (“AI-malcode”) that can mutate its code on the fly to evade detection. Trend Micro’s 2026 report warns of “polymorphic malware that constantly rewrites its own code” as a standard tool for attackers. Today’s malware may embed small machine-learning models or inference engines that make on-device decisions – for example, choosing the best lateral-movement tactics by analyzing system telemetry. Beyond that, AI aids attackers in reconnaissance and exploitation. Machine learning can sift through public code repositories or leaked patch notes to predict zero-days before they’re patched.

In ransomware, AI is enabling more autonomous operations. Trend Micro notes that next-generation ransomware may identify high-value victims and exploit pathways without human guidance, even negotiating ransom demands via automated chatbots. The result is an AI-powered extortion ecosystem: faster infection and encryption, plus self-driving communications with victims. In practice, criminals already use AI tools to decide which networks to target and how to harvest credentials efficiently. Key AI-malware and ransomware trends include:
Adaptive, Self-Modifying Malware: Malicious payloads that rewrite themselves to bypass signature-based defenses. These may use swarm or neural-network architectures internally, as recently demonstrated in academic research.
Automated Exploit Mining: AI bots scanning internet-facing services for vulnerable configurations or missing patches, then crafting exploits.
AI-Orchestrated Ransomware: RaaS operations that leverage AI for victim profiling, vulnerability chaining, and even “extortion bots” to interact with victims. For example, an AI system could autonomously select an affected company’s most sensitive data for exfiltration or identify when legal counsel might be involved, adapting its playbook in real-time.
Deepfakes and Synthetic Identity Fraud
Identity spoofing and fraud are especially ripe for AI abuse. High-fidelity deepfake videos and audio are now cheap and convincing, letting attackers mimic anyone. The Sumsub fraud report notes criminals are combining deepfakes and AI-generated documents in multi-layered schemes. One public case involved an Arup engineer transferring US$25 million after following

instructions that turned out to be a deepfake voice of his boss. Experian’s consumer survey found over 80% of people worry AI will create fake identities indistinguishable from real ones. Fraud rings now use synthetic identities (blends of real and fake data) armed with AI-generated IDs and deepfake liveness videos to bypass KYC systems. Moreover, early-stage AI fraud agents are emerging: autonomous programs capable of completing entire fraud workflows with minimal human help. These agents can spin up a fake persona, generate required documents on demand, pass through verification steps, and even learn from failed attempts to refine their tactics. In short, identity-related attacks are moving from simple spoofing into complex, AI-driven schemes. Crucial developments include:
Deepfake Impersonation: High-quality audio/video fakes used in social media, call scams, or face-authentication fraud. Criminals have already cloned voices of executives and political figures to lend credibility to scams.
Synthetic Identity Networks: Creation of new digital identities (combining stolen data with AI-generated imagery/documents) used for fraud rings and money laundering.
Autonomous Fraud Agents: AI systems that orchestrate entire verification frauds – for example, generating a synthetic persona, submitting a deepfake video for liveness checks, tampering with browsing data, and iterating until access is granted.
Executive Action
These AI-driven trends demand urgent C-suite attention. Executives must elevate AI-threats in enterprise risk assessments and resilience planning. Industry guidance emphasizes “embedding security across every layer of AI adoption” and integrating adaptive defenses with human oversight. In practice, this means updating IR playbooks for rapid, automated attacks; stress-testing systems against AI-enabled phishing; and strengthening identity governance.
Key steps for leaders include:
Enterprise Risk Assessment: Evaluate exposure to AI-enhanced threats (AI-crafted phishing, deepfake identity scams, etc.) and model attack scenarios.
Resilience Planning: Revise incident response and business continuity plans for high-velocity attacks (e.g. automated ransomware blips or data exfiltration bots).
SOC Modernization: Invest in next-gen monitoring and analytics (AI/ML-enabled SIEM/XDR) that can detect anomalous, AI-pattern attacks.
Red Team Simulations: Conduct realistic drills (e.g. deepfake spear-phishing, AI-agent penetration tests) to uncover gaps.
Governance & Training: Establish AI-use policies and conduct training so that staff recognize new tactics (e.g. “just because a video looks real doesn’t mean it’s genuine”).
MBS is uniquely positioned to help organizations prepare. We offer tailored risk assessments and strategic advisory focused on AI-era threats, helping clients prioritize investments. Our services include modernizing security operations (leveraging AI-based detection and SOAR), orchestrating red-team/blue-team exercises that simulate generative-AI attacks, and designing governance frameworks for both defensive and adversarial AI. By partnering with MBS, executives can ensure their strategies and controls evolve with the threat landscape. In a world of autonomous cyber-adversaries, proactive planning – with expert guidance – is the best defense.




Comments